0x01 背景
看着标题是不是很诧异? struct不是值类型么? 怎么是 object?
先看看一段代码, 输出的结果是是什么?
using System;
namespace StructDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyStruct myStruct = new MyStruct();
Console.WriteLine($"my struct is object:{myStruct is object}");
int a = 1;
Console.WriteLine($"int is object:{a is object}");
}
}
struct MyStruct
{
}
}
输出结果如下:
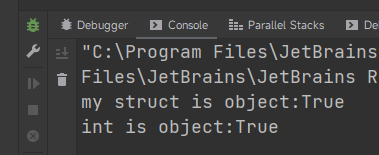
明明我们学习的时候说 struct 是值类型, 为什么代码输出 True?
0x02 文档
我们来看看微软的文档怎么来描述的: 常规类型系统 | Microsoft Docs
.NET 中的所有类型不是值类型就是引用类型。
值类型是使用对象实际值来表示对象的数据类型。 如果向一个变量分配值类型的实例,则该变量将被赋以该值的全新副本。
引用类型是使用对对象实际值的引用(类似于指针)来表示对象的数据类型。 如果为某个变量分配一个引用类型,则该变量将引用(或指向)原始值。 不创建任何副本。
.NET 中的通用类型系统支持以下五种类别的类型:
具体来说:
- 类 : 类是可以直接从另一个类派生以及从 System.Object 隐式派生的引用类型。
- 结构 : 结构是隐式从 System.ValueType 派生的值类型,后者则是从 System.Object 派生的。 对于表示内存要求较小的值以及将值作为按值参数传递给具有强类型参数的方法,结构很有用。 在 .NET 中,所有基元数据类型(Boolean、Byte、Char、DateTime、Decimal、Double、Int16、Int32、Int64、SByte、Single、UInt16、UInt32 和 UInt64)都定义为结构。
- 枚举 : 枚举是一种值类型,该值类型直接从 System.Enum 继承并为基础基元类型的值提供替代名称。 枚举类型具有一个名称、一个必须为某个内置带符号或不带符号的整数类型的基础类型(如 Byte、Int32 或 UInt64)以及一组字段。
- 接口 : 接口定义用于指定“可以执行”关系或“具有”关系的协定。 接口通常用于实现某种功能,如比较和排序(IComparable 和 IComparable 接口)、测试相等性(IEquatable 接口)或枚举集合中的项(IEnumerable 和 IEnumerable 接口)。 接口可具有属性、方法和事件,所有这些都是抽象成员;也就是说,虽然接口定义这些成员及其签名,但每个接口成员的功能由实现该接口的类型定义。 这意味着实现接口的任何类或结构都必须为该接口中声明的抽象成员提供定义。 接口也可以要求任何实现类或结构实现一个或多个其他接口。
- 委托 : 所有委托从 System.MulticastDelegate(继承自 System.Delegate)继承。 C#、Visual Basic 和 C++ 语言不允许从这些类型继承, 而是提供了用于声明委托的关键字。
0x03 分析
从上面的文档我们可以看出:
1. Object是所有类的基类
Object 类 (System) | Microsoft Docs 中提到:
支持 .NET 类层次结构中的所有类,并为派生类提供低级别服务。 这是所有 .NET 类的最终基类;它是类型层次结构的根。
其部分源码object.cs如下:
// ==++==
//
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
//
// ==--==
/*============================================================
**
** Class: Object
**
**
** Object is the root class for all CLR objects. This class
** defines only the basics.
**
**
===========================================================*/
namespace System {
using System;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Runtime.ConstrainedExecution;
using System.Runtime.Versioning;
using System.Diagnostics.Contracts;
using CultureInfo = System.Globalization.CultureInfo;
using FieldInfo = System.Reflection.FieldInfo;
using BindingFlags = System.Reflection.BindingFlags;
#if FEATURE_REMOTING
using RemotingException = System.Runtime.Remoting.RemotingException;
#endif
// The Object is the root class for all object in the CLR System. Object
// is the super class for all other CLR objects and provide a set of methods and low level
// services to subclasses. These services include object synchronization and support for clone
// operations.
//
//This class contains no data and does not need to be serializable
[Serializable]
[ClassInterface(ClassInterfaceType.AutoDual)]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)]
public class Object
{
//此处省略
}
2. 值类型是 ValueType 的子类
从valuetype.cs看到, 结构的定义代码如下:
// ==++==
//
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
//
// ==--==
/*============================================================
**
** Class: ValueType
**
**
** Purpose: Base class for all value classes.
**
**
===========================================================*/
namespace System {
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Runtime.Versioning;
[Serializable]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)]
public abstract class ValueType
{
//此处省略
}
Purpose: Base class for all value classes.
所有的值类型都是 ValueType的子类, 包括: 结构、枚举
enum.cs的源码可看出 Enum : ValueType:
// ==++==
//
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
//
// ==--==
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Runtime.Versioning;
using System.Diagnostics.Contracts;
namespace System
{
[Serializable]
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)]
public abstract class Enum : ValueType, IComparable, IFormattable, IConvertible
{
//此处省略
}
从上述的表述可以总结为下图:
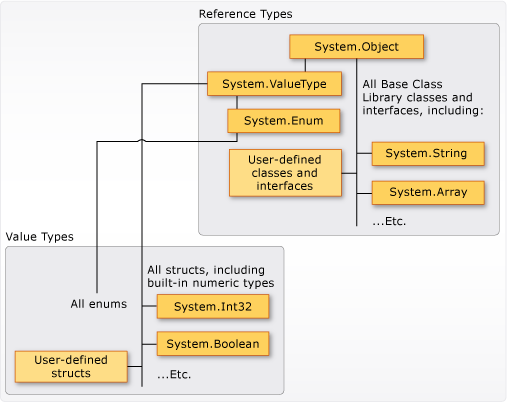
从定义上看 : 值类型都是派生自 ValueType, ValueType派生自 Object, 所以 struct is object 输出为 True.
0x04 疑问
object 是引用类型, struct 是值类型, 实际怎么判断 struct is object呢?
这里就涉及到了值类型和引用类型的转换, 即: 装箱和拆箱
而 struct is object的过程为 : struct -> ValueType(引用类型) -> Object .
1. 装箱
在微软文档装箱和取消装箱 - C# 编程指南 | Microsoft Docs 中我们可以看到:
int 1= 123;
//以下语句对变量 i 隐式应用了装箱操作:
object o = i;
此语句的结果是在堆栈上创建对象引用 o,而在堆上则引用 int 类型的值。 该值是赋给变量 i 的值类型值的一个副本。 以下装箱转换图说明了 i 和 o 这两个变量之间的差异:
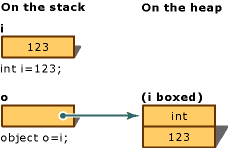
即装箱后的object,包含了值类型的原始类型和值.
2. 拆箱(取消装箱)
取消装箱操作包括:
- 检查对象实例,以确保它是给定值类型的装箱值。
- 将该值从实例复制到值类型变量中。
下面的语句演示装箱和取消装箱两种操作:
int i = 123; // a value type
object o = i; // boxing
int j = (int)o; // unboxing
下图演示了上述语句的结果:
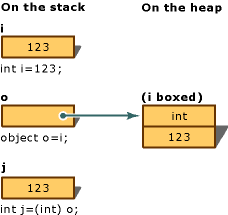
要在运行时成功取消装箱值类型,被取消装箱的项必须是对一个对象的引用,该对象是先前通过装箱该值类型的实例创建的。 尝试取消装箱 null 会导致 NullReferenceException。 尝试取消装箱对不兼容值类型的引用会导致 InvalidCastException。
下面的示例演示无效的取消装箱及引发的 InvalidCastException。 使用 try 和 catch,在发生错误时显示错误信息。
class TestUnboxing
{
static void Main()
{
int i = 123;
object o = i; // implicit boxing
try
{
int j = (short)o; // attempt to unbox
System.Console.WriteLine("Unboxing OK.");
}
catch (System.InvalidCastException e)
{
System.Console.WriteLine("{0} Error: Incorrect unboxing.", e.Message);
}
}
}
此程序输出:
Specified cast is not valid. Error: Incorrect unboxing.
0x05 总结
struct is object的过程包含了值类型到引用类型的转换, 也包含了值类型和引用类型的定义划分.- 通用类型:
- 值类型 : 对象即为本身
- 引用类型 : 对象为值的引用
其关系图谱为:

- 装箱过程

- 拆箱过程






